Bruxism and Gum Recession: Understanding the Link and Treatment Options
Bruxism, or teeth grinding, can have serious situations for your oral health, including causing bruxism gum recession treatment challenges. This condition is often linked to the gradual loss of gum tissue, leading to receding gums and increased sensitivity. When left untreated, bruxism gum recession treatment becomes essential to prevent further damage and restore the health of your gums.
In this guide, we will explore the connection between bruxism and gum recession, the symptoms to watch for, and the various treatment options available. By understanding the problem, you can take proactive steps to protect your oral health and address gum recession caused by teeth grinding.
What Is Bruxism?
Bruxism refers to the unconscious grinding or clenching of teeth, often occurring during sleep. This repetitive action puts unnecessary stress on the teeth and jaw, leading to potential damage over time. For many, bruxism is triggered by factors like stress, anxiety, or an abnormal bite. The constant pressure can cause enamel wear, jaw pain, and even contribute to bruxism gum recession treatment concerns. It is important to recognize the signs early, as untreated bruxism can worsen, leading to more severe dental issues.
The Link Between Bruxism and Gum Recession
Bruxism can contribute to gum recession by placing excessive force on the teeth and gums. The constant grinding and clenching not only wear down tooth enamel but also strain the surrounding gum tissue, leading to recession. Here is how bruxism affects your gums:
- Increased Pressure on Gums: The repetitive force from grinding can push the gums away from the teeth, leading to recession.
- Wear and Tear on Tooth Enamel: The enamel breakdown exposes the tooth roots, making gums more vulnerable to recession.
- Jaw Misalignment: Misaligned teeth from bruxism can cause uneven pressure on certain areas of the gums, accelerating gum recession.
- Inflammation and Irritation: Continuous grinding can irritate the gum tissue, causing inflammation and contributing to gum recession.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Gum Recession
Gum recession occurs gradually, and its early symptoms may be subtle, but recognizing them early is key to preventing further damage. Here are some common signs to look for:
- Tooth Sensitivity: One of the first signs of gum recession is increased sensitivity, especially when eating hot, cold, or acidic foods. The exposed tooth roots due to receding gums make them more vulnerable to temperature changes.
- Visible Tooth Lengthening: As the gums recede, the teeth may appear longer than usual. This is a clear sign that the gum tissue is pulling away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth’s surface.
- Gum Line Pulling Back: If you notice that your gums are visibly shrinking or pulling back, it is a strong indicator of gum recession. This can sometimes lead to noticeable gaps between the gums and teeth.
- Bleeding or Swelling: Gum recession can sometimes cause the gums to bleed, especially when brushing or flossing. Swelling and irritation can also be present, particularly if there’s an underlying infection or inflammation.
- Bad Breath or Foul Taste: As gums recede, they can create pockets between the gums and teeth, which may collect bacteria. This can lead to persistent bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth.
Treatment Options for Bruxism-Induced Gum Recession
Addressing bruxism-induced gum recession requires a combination of treatments aimed at both protecting the gums and managing the grinding or clenching habit. Here are some effective treatment options:
- Scaling and Root Planing: This non-surgical procedure involves cleaning the teeth and gums thoroughly to remove plaque and tartar, helping to improve gum health and reduce recession.
- Dental Bonding: For cases where the gum recession has exposed the tooth root, dental bonding can be used to cover and protect the area, improving both function and appearance.
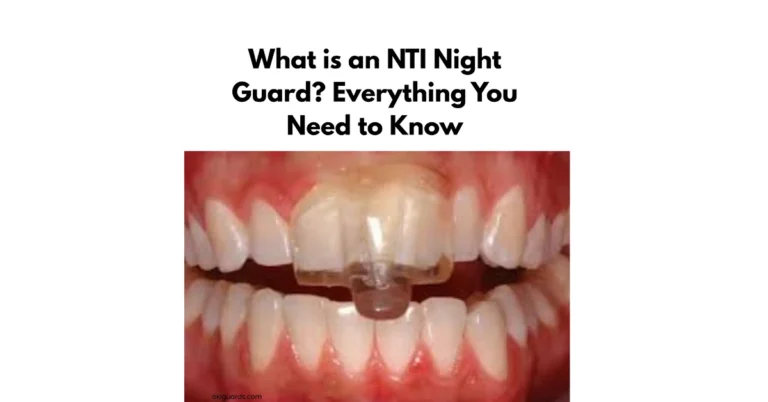
- Mouthguards or Splints: A custom-fitted mouthguard is often recommended to reduce the pressure caused by teeth grinding. Wearing a mouthguard at night can prevent further damage to the gums and teeth.
- Gum Grafting: In more severe cases of gum recession, a surgical procedure like gum grafting may be needed. This involves taking tissue from another part of your mouth or using synthetic material to rebuild the gum line.
- Gum Grafting: In more severe cases of gum recession, a surgical procedure like gum grafting may be needed. This involves taking tissue from another part of your mouth or using synthetic material to rebuild the gum line.
- Stress Management Techniques: Since stress is a major trigger for bruxism, practicing relaxation methods such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help reduce the grinding habit.
Preventive Measures to Maintain Gum Health
Maintaining healthy gums is important, especially for individuals with bruxism. By taking preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of gum recession and protect your oral health. Here are some effective strategies:
- Wear a Custom Mouthguard: A custom mouthguard can protect your gums and teeth from the pressure caused by teeth grinding, reducing the risk of bruxism gum recession treatment issues.
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent gum disease, which can lead to gum recession.
- Manage Stress: Since stress is a common trigger for bruxism, finding ways to manage stress, such as through relaxation techniques or exercise, can help reduce grinding and protect your gums from further damage.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Regular visits to the dentist help detect early signs of gum recession and bruxism, allowing for prompt treatment.
- Avoid Tobacco Use: Smoking or using tobacco products can worsen gum recession and increase the risk of gum disease. Quitting tobacco is essential for maintaining overall oral health.
FAQs
Conclusion
Bruxism can lead to significant gum recession if left untreated, but with the right treatment, the damage can be managed effectively. Non-surgical and surgical options, along with preventive measures, can help protect your gums. Early management is the key to successful bruxism gum recession treatment and maintaining long-term oral health.